Data gathering
A good preparation of the data is crucial for the success of the Map EasyMap offers various, universal data interfaces to import or to link data. However, EasyMap does not contain data entry options. Therefore, use your standard software (database, spreadsheet, statistics package, etc.) for data acquisition.
The following hints and tips are intended to help you optimize your own data for use in EasyMap.
Perform complex calculations externally
EasyMap offers some functions for data calculation. However, a program such as EasyMap, which specializes in map graphics, can understandably not contain the scope of performance of an Excel or a database program. Therefore, before you transfer data to EasyMap, perform all complex data calculations (e.g. indices, quotas, target/actual deviations, proportions, etc.) with your standard software.
Primary Key
For some functions EasyMap needs a primary key in the data. This is used to uniquely identify the data. A column that is to be used as the primary key must therefore contain an entry in each line; all values must be different (i.e. duplicates are not permitted). For example, customer numbers, postal codes, municipal codes, etc. can be used as primary keys. A primary key is often defined in database tables. EasyMap then automatically adopts this primary key. Another primary key cannot then be used for such a table.
Note: With location-specific analyses, the symbols and diagrams resulting from this table can be moved and their properties (e.g. display with original position or labeling) can be individually adapted.
Table structure
Create your data in a two-dimensional table, where the rows reflect the geographical structure of the data, while the columns contain the attributes and data values (database tables are not called rows, but records; columns are called fields). With text files and tables from calculation programs (e.g. Excel), make sure that all rows have the same structure and that there are no different data types within a column (e.g. numbers and text mixed together).
Note: EasyMap has no limit to the number of rows or columns in the data table. You do not need to sort the data to transfer it to EasyMap.
Provide data in a suitable file format
The easiest way to transfer data to EasyMap is often to copy the data to the clipboard (e.g. mark data cells in Excel and then copy them). EasyMap can then import the data from the clipboard. Of course, EasyMap can also read standard formats (e.g. xlsx/xls, accdb/mdb, txt, csv). If your data is in a format or in a system that is not supported by EasyMap, export your data to a suitable format or to the clipboard or provide the data via ODBC interface.
Tips for Using Excel Tables
When Excel tables are ready for printing, they are sometimes difficult for EasyMap to process. Elaborately designed multiline column headers or pre-columns, linked cells and multiline totals rows and footnotes can cause EasyMap to not always correctly recognize the structure of the columns containing the data to be used. In such cases it is recommended to define the main set of numbers in Excel as Named range.
Avoid columns that contain different data types (e.g. texts and numbers) or differently formatted content. For example, if Excel provides a column of numbers for EasyMap, but these contain text in some cells, Excel will return empty cells instead of the text. This problem occurs occasionally when Excel users have not found another way to display postal codes with a leading zero than to enter the postal code as text.
If an Excel table is password-protected, it cannot be imported into EasyMap. When importing, you receive an error message that the file does not have the expected format. In this case, save the Excel table without password protection or use the clipboard.
What to do with P.O. box and large recipient postal codes?
The digital postcode maps usually only contain the areas for the delivery item part numbers. P.O. box and large recipient postal codes are not included in the maps, nor are any other special postal codes (e.g. promotional postal codes). If postcode maps are used as a map basis, this means that all data that does not contain a delivery postcode cannot be assigned to the map. Remedy: If your data source (e.g. the customer database) contains separate fields for delivery and P.O. box postal codes (e.g. delivery address and billing address), please select the field containing the delivery postal code for use in EasyMap. If this option is not available, you can use EasyMap to convert the German P.O. box and large recipient postal codes into delivery postal codes.
It's like this:
In addition to the address data, import the Excel file, which is delivered and installed together with the digital postcode map. This is located in the directory in which the digital postcode map is also installed. You can find this directory by clicking on the arrow in the upper right corner of the control window Base Maps.
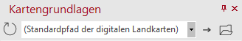
You can also open the table directly via the context menu More information in the control window Base Maps. The file has the same file name as the digital postcode map and the extension xlsx (e.g. DPLZ1612.XLSX). The Excel file contains several spreadsheets. The required information can be found in the worksheet Assignment to delivery postcode. It contains in column A every valid 5-digit postcode, in column B the type of postcode and in column C the assigned delivery postcode (for P.O. box postcodes this is the delivery postcode to the P.O. box location, for large recipient postcodes this is the delivery postcode to the company location). When importing the table, please remember to format columns A and C in EasyMap with the postal code (Germany) format.
In the table that contains the postal codes that cannot be used, add a data column with the Lookup Using Reference Table function.
The figure shows the necessary settings:
In this example, the new column is named "Delivery postal code". In this example, the column with the non-usable postal codes in your original table is called "Postcode". The external data table "Assignment to delivery postal code" is used as the reference table. For all postal codes found in the reference table in the lead column, the value is taken from the value column and entered in the new data column in your source table.
Geocoded data
Enrichment of address databases by geographic coordinates (longitude and latitude), e.g. with the LT GeoCoder. The addresses are not only geocoded, but also validated and provided with extensive documentation of the quality of the geocoding.
Fields of application:
- precise visualization of locations in maps
- Location and branch network planning
- distance calculation
- Planning of visit tours in the field service
For further information or an online presentation on the LTGeoCoder please visit our website.